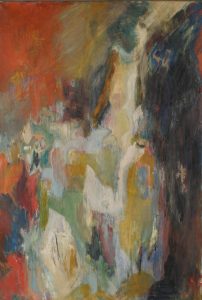Microcosmism
Fig 1 Logo of the Club of Rome: a microcosm of humanity on Earth.
In April 1968, a group of thirty individuals from ten countries,scientists, educators, economists, humanists, industrialists, and national and international civil servants, gathered in the Accademia dei Lincei in Rome. They met at the instigation of Dr. Aurelio Peccei, an Italian industrial manager, economist, and man of vision, to discuss a subject of staggering scope; the present and future predicament of humanity. Out of this meeting grew The Club of Rome, an informal organization that was aptly described as an “invisible college.” Its purposes were to foster understanding of the varied but interdependent components, economic, political, natural, and social-that make up the global system in which we all live; to bring that new understanding to the attention of policy-makers and the public worldwide; and in this way to promote new policy initiatives and action. The predicament now is how to address climate change in order to live sustainably. With respect to new actions, this blog addresses the question, what is the role and the potential of the arts in bringing about the cultural change required to live within Earth’s ecological limits? That was the question pursued by Melita Rogelj as her Master’s thesis for the School for International Training in Vermont (graduated in 2000).
Rogelj set out to answer the following questions in her research:
- What is the connection between the arts and sustainability?
- What is a new way to think about the arts that would inspire and facilitate a transition to increased levels of sustainability?
- What is the importance of art for sustainability?
Her approach was:
“…… to associate sustainability with cultural evolution. In order to achieve sustainability, I believe we must become a society of artists, willing to take creative risks, attempting to make connections and leap across disciplines and cultures in ways previously not attempted, or even imagined.”
There is an urgent need to develop the underlying theory and principles of “sustainability science,” based on an understanding of the fundamental interactions between nature and humans. This requires a new research and education paradigm that embraces biocomplexity, integrates the physical, biological, and social sciences, and uses a coupled, human–natural systems approach. For this purpose, a cross-cultural, interdisciplinary mindset is needed to enlarge the discursive space of museums, schools, universities, disciplines and collections of objects by pushing at their conceptual boundaries. The knowledge produced from objects such as works of art is quite distinct from textual knowledge. But while we would like to believe that sharp boundaries define the functions of knowledge objects each is really the tip of an interdisciplinary iceberg. Objects are the basis for thinking about microcosms, where the object stands for much deeper thought. ‘Microcosmic’ refers to the idea that parts or relations that define an entity are discovered, summarised, or miniaturised, in some smaller unit, which thereby becomes a cultural object (Fig 1).
According to Rudolf Allers microcosmism may be defined in the following way:
“One vague and broad conception is shared by all authors who ever speculated on the microcosmus and its relation to the macrocosmus. The former, which the Latin authors usually call minor mundus, has certain features or principles in common with the macrocosmus or the universe.”
Hence, the basic idea of microcosmism is that it is a movement to promote the study of correspondence or similarity between two entities on the assumption that the smaller entity is easier to investigate that the larger.
Works of art are microcosms. To meet Melita Rogelj’s objective, the universal language of art has to be harnessed to inspire individual action. This means drawing attention to the current environmental crisis and to moving people to change the behaviours and habits that contribute to it. This blog is a first attempt to explore the the role of microcosmic art to communicate an emotional experience.
Expressing artful spirituality
In previous blogs, Corixus addressed transformation, or metamorphosis, as the concept central to making and adding meaning in abstract art.
http://corixus.tumblr.com/post/163441434503/microcosms-in-the-hand
http://corixus.tumblr.com/post/178075044163/transformation-in-art
This blog is about art as a carrier of two kinds of intelligence required to live sustainably. These were defined seven centuries ago by the Sufi poet Rumi. The first he defined acquired knowledge or book learning. It is the kind of intelligence that helps us to manage our environment and is tested to see how well we retain information. Rumi describes it as “getting always more marks on your preserving tablets.” This is the intelligence of our schooling and striving to succeed. It is imparted by narrative art which is a microcosms of the outer world expressing situations and objects.
Rumi also describes another kind of intelligence: “one already completed and preserved inside you./ A spring overflowing its springbox.” This intelligence is not the kind that moves from the outside in, as in traditional learning. “This second knowing is a fountainhead from within you, moving out.” This intelligence originates from within us rather than from outside sources. It is imparted by abstract art which is a microcosm of the inner world of thoughts and ideas expressing creativity and transformation. In this respect, creativity and culture are virtually interchangeable.
In earlier times spiritual messages were transmitted figuratively directly through stained glass. But abstraction has entered the interface between spirituality and people (Fig 2).
Fig 2 A microcosm in stained glass inspired by the cellular basis of anatomy
From the maker’s and viewer’s perspective transformation provides access to deeper aspects of ourselves, including the pre-verbal feelings and symbols that reside in our subconscious. So, we make and pursue transformations in search of the one realm within which all things are connected. For painting, this realm is the canvas before us. In other words, producing and viewing an abstract work can be a meditative, almost mystical affair. The work has aesthetic qualities expressing ideas and emotions in a two-dimensional visual language. The elements of this language—its shapes, lines, colours, tones, and textures—are used in various ways to produce sensations of volume, space, movement, and light on a flat surface. These elements are combined into expressive patterns in order to represent real or supernatural phenomena to interpret a narrative theme, or to create wholly abstract visual relationships.
Despite being without a material reference point, abstract art nevertheless often carries deep messages from the artist and are also injected by the viewer. In fact the beginnings of modern art, especially abstract art, have strong spiritual roots. This fact is not always obvious from textbook presentations, which are more likely to focus on the timeline of innovations of the twentieth century. While these historical narratives are valid they omit what may have been the most central motivation of the pioneers of abstract art who shared common spiritual roots. For many of these artists art was primarily about spirituality, and was perhaps the most appropriate vehicle for expressing and developing that spirituality. Kandinsky expressed this conviction in his 1912 publication “Concerning the Spiritual in Art”; Mondrian mentions it in many of his writings; and so do other painters, poets, musicians and dancers. Here is Kandinsky, in a selection from his influential 1912 booklet Concerning the Spiritual in Art:
“When religion, science and morality are shaken and when outer supports threaten to fall, man withdraws his gaze from externals and turns it inwards”.
“Literature, music and art are the most sensitive spheres in which this spiritual revolution makes itself felt. They reflect the dark picture of the present time and show the importance of what was at first only a little point of light noticed by the few. Perhaps they even grow dark in their turn, but they turn away from the soulless life of the present toward those substances and ideas that give free scope to the non-material strivings of the soul”. (Concerning the Spiritual in Art, p. 33)
This was also admitted by the painter Mark Rothko when he said in 1957:
“I am not interested in any relationships of colour or form or anything else, I am interested in the basic human emotions – tragedy, ecstasy, doom, and so on, and the fact that lots of people break down and cry when confronted with my pictures shows that I communicate with those basic emotions. The people who weep before my pictures are having the same religious experience I had when I painted them.”
The more one looks at Rothko’s great monochrome canvases, such as the Rothko Chapel pictures (Fig 3), the more you see subtle shifts and nuances of brush marks and hue. But what is the connection between seeing more evidence of the painter’s mystical handicraft and the emotional response? Emotional responses are generally regarded as the keystone to experiencing art, and the creation of an emotional experience has been argued as the purpose of artistic expression. Research has shown that the neurological workings of perceiving art differ from those used in standard object recognition. Instead, brain regions involved in the experience of emotion and goal setting are activated when viewing art.
Fig 3 A viewer in the ‘Rothko Chapel’.
The Rothko Chapel is a non-denominational chapel in Houston, Texas, founded by John and Dominique de Menil. The interior serves not only as a chapel, but also as a major work of modern art. On its walls are fourteen black but colour-hued paintings by Mark Rothko
Mark Rothko is classified as one of the early New York abstract expressionists, a group of New York painters of the late 1940s and ’50s, all of whom were committed to an expressive art of profound emotion and universal themes. Abstract expression blended elements of Surrealism and the first abstract art in an effort to create a new style fitted to the postwar mood of anxiety and trauma. The movement embraced the gestural abstraction of Willem de Kooning and Jackson Pollock, and the colour field painting of Mark Rothko and others. Gestural abstraction, sometimes called action painting, is a style of painting in which paint is spontaneously dribbled, splashed or smeared onto the canvas, rather than being carefully applied. The term colour field painting is characterised by large areas of a more or less flat single colour. Both techniques introduce random elements of form, tone and colour placement.
Small is large
Ruth Abrams (1912-1986) is a key artist of the time. She also belonged to the New York group of abstract expressionists although her work remains on the fringes of the movement. She may be described as a metamorphic artist in that throughout her career she moved confidently between figuration and abstraction. The more traditional scenes of painting offered a continual starting point for transformation. The most striking and successful example of this kind of metamorphosis is “Memory of My Mother,” a 1947 painting featuring an outline resembling a woman dissolving into a striking network of interlocking and interwoven colours (Fig 4).
Fig 4 ‘Memory of my Mother’, Ruth Davidson Abrams ca. 1959 Collection of Yeshiva University Museum Gift of the Estate of Ruth Abrams (2006.079)
However, it is believed by many that Abrams’s crowning achievement in abstract art is a series she produced in the 50s and 70s entitled “Microcosms.” The paintings describe the progression of an aesthetic journey —a discovery of a personal vocabulary based upon our unearthly perception of a universe distinctly different from familiar earthbound views and horizons. These are works on tiny canvases, some as small as postage stamps, in which, through microscopic swathes and strokes of colour, she transcribed her thoughts about space exploration to produce imaginary interstellar meditative landscapes. Abrams chose the word microcosm to describe her artistic creations because they represented in miniature the characteristics of something much larger, namely, the cosmos as a place, or situation to which we turn when meditating on origins and futures. In a strange way the very small pictures draw the viewer into interstellar space.
Fig 5 Andromeda nebula (1900)
With respect to the timing of these works, Abrams was responding to black and white photographic images of outer space that had begun enter the public domain through books on astronomy and space science at the beginning of the 20th century. The Andromeda “nebula,” had been photographed at the Yerkes Observatory around 1900 (Fig 5). To modern eyes, this object is clearly a galaxy. At the time, though, it was described as “a mass of glowing gas,” its true identity unknown. Seventy-five years after this first image of Andromeda, NASA launched one of the most ambitious experiments in the history of astronomy: the Hubble Space Telescope, which has so radically changed and enlarged our pictorial understanding of the cosmos. On April 1, 1995 Hubble captured a small region of the Eagle Nebula, a vast star-forming region 6,500 light-years from Earth. A colour version, called Pillars of Creation, was released from NASA in 2015 (Fig 6). Ruth Abrams died in 1986 and we are left to speculate about what her artistic response would have been to later space probes.
Fig 6 Part of the Eagle Nebula; NASA/ESA/Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA)
Abrams explaining how she came to paint this vast entity in miniature said;
“I realized I could never do anything as big as the bigness I was now aware of, and that paradoxically, in order to convey that bigness, I had to move away from it and paint small.”
Her work is evidence of the paradox that a tiny canvas can convey the giant wonder of the cosmos (Figs 7-9).
Fig 7 Ruth Abrams microcosm; a cropped enlargement
Fig 8 Ruth Abrams microcosm; a cropped enlargement
Fig 9 Ruth Abrams handling one of her Microcosms
Transforming Mondrian
Like Abrams’ microcosms, Piet Mondrian’s paintings had no narrative content and represented a metamorphosis over a period of years from his paintings of windmills and trees. His lines and colours gradually became the subjects and he argued that they were were the purest forms of expression. He elaborated this belief in his long essay ‘Neo-Plasticism in Pictorial Art’ published in the first eleven issues of the journal De Stijl. He wrote:
“As a pure representation of the human mind, art will express itself in an aesthetically purified, that is to say, abstract form. The new plastic idea cannot therefore, take the form of a natural or concrete representation – this new plastic idea will ignore the particulars of appearance, that is to say, natural form and colour. On the contrary it should find its expression in the abstraction of form and colour, that is to say, in the straight line and the clearly defined primary colour”.
Mondrian’s art was not based on reasoning or calculation. Intuition was central to his concept of the artistic process – but he always had a strong urge to position his art in a wider cultural and philosophical context. Crucial to Mondrian’s thought was the Theosophical notion of evolution, which required the transformation of old ideas to make room for the new, in life, in society and in art.
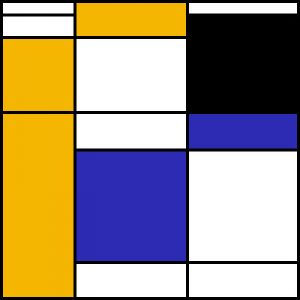
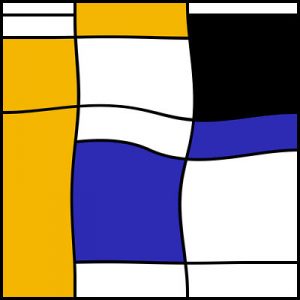
Using software tools comprising algorithms and digital filters, Corixus is exploring futures of the Mondrian abstract style, introducing anatomical curves, tones and textures at random to produce microcosms (Figs 10-12) ).
Fig 10 Random composition in black blue and yellow (Corixus. 2018)
https://jef.works/mondrian-generator/
Fig 11 Transformation of Fig (Corixus. 2018)
PaintShop Pro
Fig 12 Transformation of Fig (Corixus. 2018)
Topaz Simplify.
The responses of viewers to these three images are overwhelmingly to place the last transformation first.
Anatomical microcosms
The starting point for this research into the transformation of Mondrian’s style is the concept of cultural ecology in which artistically created microcosms are positioned to link environment with society, In this context, Leonardo da Vinci was the first to apply the term microcosm to promote the idea that people are part of nature. He envisaged the great picture chart of the human body he had produced through his anatomical drawings as a cosmografia del minor mondo (“cosmography of the microcosm”). He believed the workings of the human body to be an analogy, in microcosm, for the workings of the universe. Leonardo wrote:
“Man has been called by the ancients a lesser world, and indeed the name is well applied; because, as man is composed of earth, water, air, and fire…this body of the earth is similar.”
He compared the human skeleton to rocks (“supports of the earth”) and the expansion of the lungs in breathing to the ebb and flow of the oceans.
Leonardo’s few full-body figures deserve attention because they reflect so well his remarkable progression as thinker and artist from medieval, through early humanist, to modern humanist ways of understanding and representing the human body as an integral part of nature. A careful look at these figures provides a visual framework for discussing the concept of a microcosm in the continuing emergence and development of Renaissance humanist ideas.
“In [the] figures there shall be revealed to you the microcosm on the same plan as before me was adopted by Ptolemy in his cosmography”.
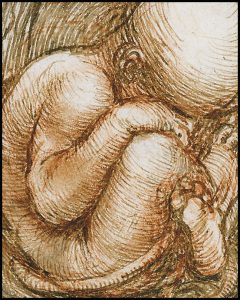
In so designating these regions of the body, Leonardo incorporates a third medieval tradition: the principle of the microcosm and the macrocosm, which held that the structure of the human body, a small world in itself, reflects the divine order of the universe (Fig 13).
Fig 13 A near-term human fetus. Leonardo da Vinci
This was no doubt in his mind when he urged us to contemplate ageing wall plaster as a stimulus to thinking about the bigger picture of patterns in and from nature. Ever since Leonardo da Vinci urged artists to search for inspiration in the dirt on walls or the streaked patterns in stones, they have found that the accidental blot, the chance mark, or the naturally occurring stain can be a starting point for some extraordinary art (Fig 14)
https://www.pinterest.co.uk/zygeena/1-patterns-in-and-from-nature/
Fig 14 Splash on the wall ?
Abstract drawing
In its blog for 15 Nov 2016 the online gallery ‘Ideelart’ showcased ten ‘unforgettable examples of abstract drawing’
Drawing was introduced as is one of the simplest and most accessible ways to make in art.
“Almost anyone can do it. All it takes is a writing implement and a flat surface. Yet as simple as the medium can be, some of the most unforgettable abstract artworks are abstract drawings packed with ambiguity and storytelling that trigger questions about their meaning
Abstract drawings are immediately approachable and direct. They are inherently ambiguous and invite a certain amount of conjecture. Ambiguity is an attraction, because it allows for the unfettered participation of anyone willing to open up to a work of art. Because they are produced in their least guarded moments they casually drew something that expressed the truest nature of their ideas from deep within. Many artists turn to drawing in order to express some essential concept they are struggling with, and suddenly a form, a gesture or a composition emerges that perfectly expresses the essence of their search (Fig 15).
Fig 15 Elaine de Kooning – Unused preparatory drawing from In Memory of My Feelings, Ink on acetate, 13 7/8 x 11 in, 1967
Picasso stretches reality and exaggerates certain features, distorting the form to better communicate the essence (Fig 16)
Fig 16 Less is more. Detail from page of a Picasso sketch book
Internet references
https://forward.com/culture/161490/art-of-ruth-abrams-deserves-second-look/
http://emptyeasel.com/2007/04/17/piet-mondrian-the-evolution-of-pure-abstract-paintings/
http://www.rogerbissell.com/id11p.html
https://www.huffingtonpost.in/afzal-ibrahim-/understanding-minimalist-_b_9037110.html
https://www.ideelart.com/magazine/abstract-drawing
http://donellameadows.org/archives/beautiful-world-a-bridge-between-the-arts-and-sustainability/
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/BF01205452
https://agendatwentyone.wordpress.com/2010/06/28/the-club-of-rome-where-the-buck-stops/